Preliminary Course
Botany. Architectural Analysis
Axis typology.
Continuous and rhythmic growth
-
Continuous growth
-
In continuous growth, both organogenesis and elongation are continuous, stable and regular.
Axis length increases and leaf appearances are regular.
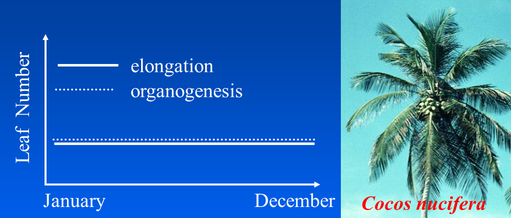
Continuous growth
Elongation follows organogenesis and both processes are stable and regular as shown by the coconut palm (Drawings and Photo D. Barthélémy, CIRAD)
Rhythmic growth
-
In rhythmic growth, organogenesis is not continuous, showing pauses between organ creation phases.
Elongation is also periodic. Rhythmic growth builds growth units, corresponding to organogenesis cycles.
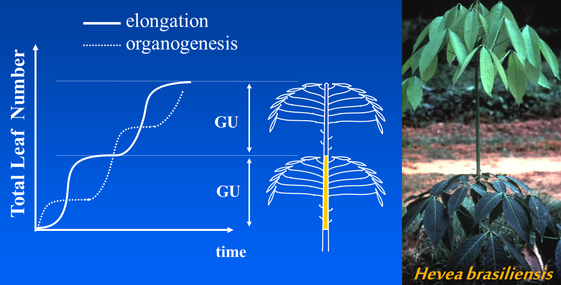
Rhythmic growth (Drawings and Photo D. Barthélémy, CIRAD)
Organogenesis is not continuous, and, on the rubber stem elongation occurs with a constant delay
Rhythmic growth: pre-formation and neo-formation processes
In the case of rhythmic growth, all the metamers and organs of the future elongated shoot may be present at an embryonic stage in a bud before the elongation of the shoot deriving from it. In this case the shoot is referred to as pre-formed and its constitutive organs as pre-formed organs or the pre-formation process.
In other cases of rhythmic growth, more organs than those included at an embryonic stage in the bud can be elongated: these supplementary, non-preformed elements are referred to as neo-formed organs or the neo-formation process.
This terminology was introduced by Hallé and al. in 1978, but first referred to by Critchfield, in 1960, defining early leaves and late leaves for pre-formed leaves and neo-formed leaves, respectively.
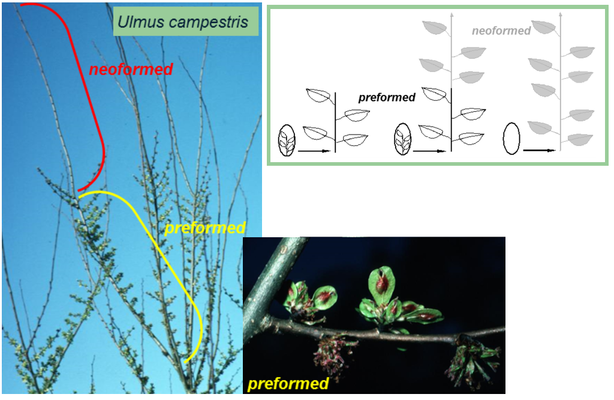
Pre-formed and neo-formed shoots (Photo and drawings D. Barthélémy and Y. Caraglio, CIRAD)
Top, right: pre-formed, pref-ormed and neo-formed, neo-formed leaves and their elongated shoots.
Left: pre-formed and neo-formed shoot portions on a young tree, showing different characteristics on the pre-formed shoot portion.
Bottom, right: Close up of a Field Elm pre-formed shoot.
Bibliography
Hallé, F., Oldemann, R.A.A., Tomlinson, P.B. 1978. Tropical trees and forests. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Critchfield W.B. 1960. Leaf dimorphism in Populus trichocarpa. American Journal of Botany, 47, pp. 699-711.
Definition
Preformation
Botany. In rythmic growth, qualifies a shoot (a growth unit part) those componants are preformed in the bud before elongation. See also NeoformationDefinition
