Preliminary Course
Applied Mathematics
Parameter estimation
Least square estimation
-
Identification of dynamic systems
- ω = 1 assigns the same level of importance to all data
- ω = 0 eliminates a datum deemed not relevant
- ω = max(Yobs)2 , the square of the maximum experimental data for a given observable reduces the effect of having observations of different orders of magnitude
- In the linear case, the best unbiased estimator of P is obtained taking weights inversely proportional to the variance of each observable.
Given a system S described by a model M(X, P, U) and a set of measured experimental data Yobs, the parameter estimation of M consists in finding a set of parameters Þ that minimizes a distance measure between Yobs and Y = g(n, Xn(Un, P, n), P).
A scalar function J needs therefore to be defined to measure the distance between model predictions and experimental data.
Quadratic cost functions are the most commonly used:
J(P) = (Yobs - Y(P))t Ω (Yobs - Y(P))
Ω is a nonnegative definite symmetric weighting matrix. The weighting coefficients located in the diagonal of the matrix are positive or zero and fixed a priori. The choice of the weights will express the relative confidence in the various experimental data and the consequent importance attached to the model performance with regard to each observable:
The solution P* = argmin J(P) is regarded as the weighted least squares estimator.
This is an optimization problem that is generally non-linear and not analytically tractable and that can be solved using local or global numerical methods (simplex, Nelder-Mead, Newton; genetic algorithm, simulated annealing, particle swarm optimization, etc).
Exercise
-
The growth rate of a fruit was modelled by a beta density function
and virtual measurements (red dots) were simulated with an additive centred Gaussian noise.
Expansion time is equal to 5.
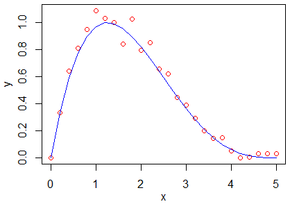
Fruit growth rate modelling (Graph V. Letort - Le Chevalier, ECOLE CENTRALE PARIS)
- The blue line represents the 'true' model (a beta density function)
The red dots stand for virtual measurements (simulated with an additive noise)
The model is expressed as follow:
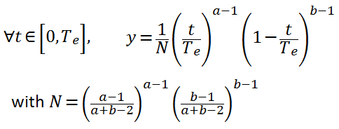
The resulting data (17 measurements) are given below.
-
x y
0.0 0.00
0.3 0.48
0.6 0.86
0.9 0.99
1.2 1.01
1.5 0.91
1.8 0.85
2.1 0.77
2.4 0.77
2.7 0.41
3.0 0.42
3.3 0.22
3.6 0.23
3.9 0.02
4.2 0.04
4.5 0.00
4.8 0.05
Using the unweighted (Ω = Identity) least squares method, find estimates for the values of a and b.
Enter the values found for a and b with one decimal and validate.
The following website can be used:
http://statpages.org/nonlin.html .
Indications using this online tool:
- Enter the number of data points, variables and parameters
In order to simplify the equations, translate both a and b values of one unit.
- The function can thus be entered (copy and paste) as follows:
Power(x/5,a) * Power(1-x/5,b) / ( Power((a/(a+b)),a)* Power((b/(a+b)),b) )
- According to the distribution shape, initialize a and b values
- Set the fractional adjustment factor to 0.2
Copy the observed values and paste them in the Text Data Editor . Separate x and y values by a comma
Click iterate button until reaching stable parameter values.
Report the estimated parameter values.
