Preliminary Course
Botany. Architectural Analysis
Preliminary Architectural Concepts.
Plant growth and development result from the activity of meristems.
Structure establishment results from primary growth, while growth thickness results from secondary growth.
The shoot apical meristem
A (shoot apical) meristem is a set of embryonic cells situated at the apical part of each axis.
These particular cells are always able to divide and thus to generate new cells, which can then differentiate into specialized cells constituting tissue (pith, epidermal tissue, vascular bundles, etc.) or leaf organs.
The division activity of meristematic cells also generates small sets of embryonic cells: the axillary meristems from which lateral shoots grow.
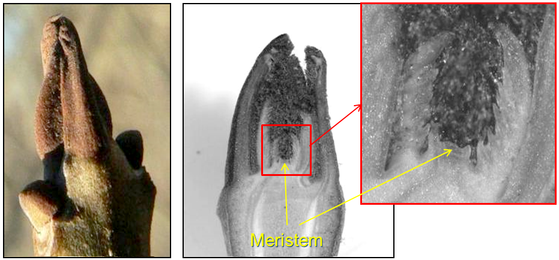
The bud. Fraxinus excelsior (Photos: Y. Caraglio, CIRAD)
Left: An apical bud. Middle: microscopic view of the apex.
Right: zoom centred on the meristem.
Two elementary processes lead to tree development: growth and branching.
Growth
-
The growth process originates in the apical bud where the apical meristem tissue is located.
At this place, cell division and elongation take place to generate new elements of the leafy axis (node, internode, leaf, axillary bud), which expand when buds break.
Growth thus involves two different consecutive processes: organ formation, called organogenesis, and organ expansion (extension phase).
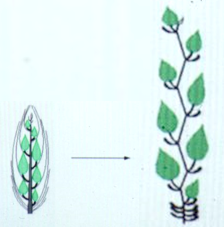
Organ formation and organ expansion on the beech tree.
Leafy axis formation starts in the bud in late autumn, while expansion (left) occurs the following spring.
(Fagus sylvatica, drawing E. Nicolini, CIRAD)

Organ expansion. (Acer pseudoplatanus, photo Y. Caraglio, CIRAD)
Left: the closed terminal bud
Right: four steps of a leafy expansion (with its leaves).
Definition
Primary growth
Botany. Primary growth is the growth that occurs as a result of cell division at the tips of stems and roots, and that gives rise to primary tissue building axes.The primary growth of a plant is the result of several processes that can be grouped into two distinct, but coordinated morphogenetic events: organogenesis and extension (Champagnat et al., 1986).
Definition
