Preliminary Course
Botany. Architectural Analysis
Architectural Unit
The Architectural Unit
-
Focusing architectural analyses on particular traits on each type of axis elaborated during plant development
usually leads to the stem (trunk) being distinguished from other axes, such that each set of axes exhibits
specific features (on young trees).
A schematic representation of the plant body can be made, a diagrammatic representation, completed by a table describing all the distinctive traits of the categories identified within the tree architecture.
This set of information (diagram and table) constitutes the architectural unit (Edelin, 1977, Barthélémy et al., 1991).
The Architectural Unit can be seen as the detailed, specific expression of its architectural model. The Architectural unit of a given species is defined from a set of constitutive axis categories of this species.
The structure and function of each category is characteristic of its rank, and for each species the number of axis categories is finite.
Identification of the architectural unit is achieved by a complete diagnosis of the functional and morphological features of all its axes categories, including the four typological morphological features (growth, ramification, direction, sexuality), but not limited to these.
The architectural unit represents the fundamental architectural and functional elementary unit of any given species.
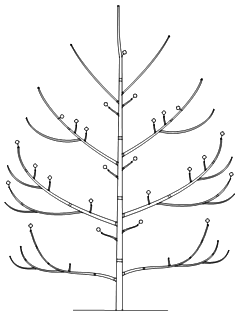

Juglans nigra (Drawings S. Sabatier, CIRAD).
The = symbol stands for growth unit limits, while the o symbol stands for female inflorescence
Left: Juglans nigra diagrammatic representation of its Architectural Unit.
Right: a young Juglans nigra (drawing).
Top, right: close-up on the tip of the main stem, showing the sympodial growth.
| Axis 1 (trunk) | Axis 2 (branches) | Axis 3 (twigs) | |
| Growth direction | orthotropic | oblique, nearly orthotropic | no preferential direction |
| Phyllotaxis | alternate spiral | alternate spiral | alternate spiral |
| Branching | rhythmic, acrotonic | rhythmic, hypotonic | rhythmic, amphitonic and epitonic |
| Growth (rhythmic) |
long annual shoots polycyclism |
long annual shoots | short annual shoots |
| Sexuality | terminal for female, lateral for male | terminal for female, lateral for male | terminal for female, lateral for male |
Bibliography
Edelin C. 1977. Images de l'architecture des conifères. Thèse de Doctorat (Sciences biologiques option Biologie végétale). Université de Montpellier II, 255 p.
Barthélémy, D., Edelin, C., Hallé, F. 1991. Canopy architecture, in: Raghavendra A.S. (Ed.), Physiology of trees, John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, 1991, pp. 1-20
Definition
Architectural Unit
Botany. The architectural Unit of a given plant species is the specific expression of its architectural model. The architectural Unit of a plant can be seen as a hierarchical branched system in which the axes can be grouped into categories according to their morphological, anatomical or functional distinctive features (Barthélémy et Caraglio, 2007).See also: Architectural Model.
