GreenLab Course
Development
Structure construction
Axes of development lists define the basis of structure construction in the GreenLab model.
Axis of Development representation
-
The axis of development state list can be easily represented as a part of an axis, with a simplified geometry.
- Attributes can be reported for each awakened state.
So far, we have encoded the physiological age of the axillary in the previous examples.
But other characters are worth encoding such as:
-
- branching delay
- other organs (leaves, sexuality), etc.
In our representation examples, the underlying geometry is simple.
For instance, in our examples, all states are represented by a rectangular cell, with a unit length, and a width reversely propotional to the ontogenetic age.
Axillaries are shown with an insertion angle of 90 degrees, and 60 degrees for leaves.
Cell colours reflect the status: grey if virtual (no phytomer, corresponding to a rest), blue if phytomer physiological age is 1, green for 2, red for 3, red for 4, etc.
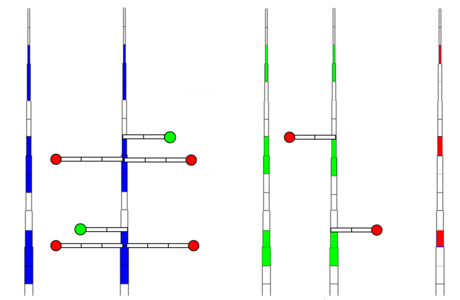
An example of axis of development representation (Drawings M. Jaeger, CIRAD)
- This rhythmic growth example shows three physiological ages for a temperate species
From left to right:
Physiological age 1 axis of development. Cells in blue stand for phytomers, while grey stand for a rest cycle.
Physiological age 1 with its axillaries. Note the branching delays, allowing synchronisation for the next growth cycle.
Physiological age 2 axis of development. Cells in green stand for phytomers.
Physiological age 2 with its axillaries.
Physiological age 3 axis of development. Cells in red stand for phytomers.
Structure reconstruction
-
The set of axes of development allows implicit and explicit structure reconstruction.
Axis development
-
The successive states describing a specific axis in the plant structure can be retrieved from its corresponding
axis of development (same physiological age). It is in fact a simple copy, with an offset corresponding to the
ontogenetic age.
This copy ends at the shorter term derived from:
- plant age,
- a transition to a higher physiological age,
- a termination specified in the axis of development (determinate growth, or death)
Axis branching
-
The branching process is a similar operation, except that the corresponding axis
of development is defined by the physiological age of the axillary (and not the bearer's age)
Reconstruction representation
Using the simple axis of development representation framework, it is easy to build flat (2D) structure schemes.
In such representation, branching angles are set at 60 or 45 degrees for better visibility.
The rest periods (in grey) are interesting to visualize, defining the chrono mode view, showing the structure framework from a chronological point of view.
While skipping the grey cells, i.e. skipping the rests, offers a more realistic view, representing only the phytomers, underlying the structure's "real" topology, defining the topo mode view.
These modes are illustrated below.
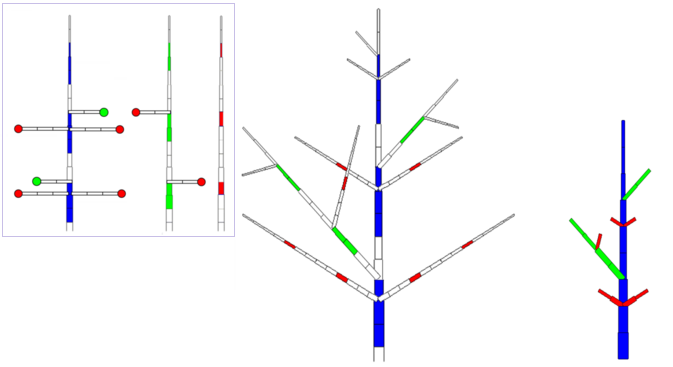
An example of structure reconstruction (Drawings M. Jaeger, CIRAD)
- This example is a reconstruction derived from the axes presented above.
Left: the 3 axes of development.
Middle: representation of the structure reconstruction in chrono mode.
Right: representation of the structure reconstruction in topo mode, skipping the rests.
The three axis of development are partially copied to define the overall structure.
