GreenLab Course
Development
Physiological age and reiteration (reminder).
Plant structure shows a different axis typology depending on the branching level or other anatomical criteria related to terminal bud differentiation.
Physiological age and reiteration
Physiological age
-
In architectural botany, the level of axis differentiation can be characterized by a physiological age.
A given physiological age is associated wih specific morphological and phenological traits, such as axis orientation, sexuality occurrence or not, specific branching patterns, etc.
Reiteration
-
As the plant develops, at mature stages the structure developing according
to the architecture unit may duplicate.
This specific branching case is called reiteration.
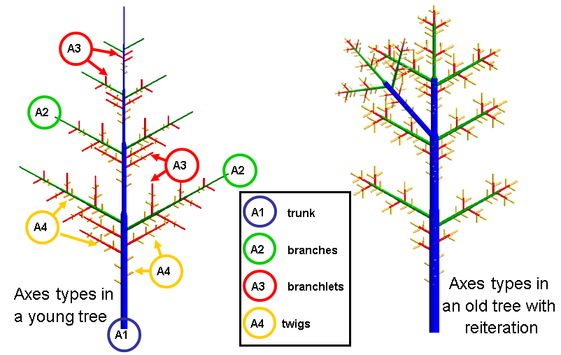
Physiological age and reiteration (Drawing M. Jaeger, CIRAD)
-
In the above example, four physiological ages are used to define the axis typology.
- Physiological age 1, in blue, characterizes the vigorous axis (such as the trunk)
- Age 2 in green stands for the branches
- Physiological age 3 is coded in red for the branchlets
- In yellow physiological age 4 stands for the twigs.
This colour code (with the colour magenta for physiological age 5) is used as a standard in GreenLab modelling representations.
Left, the axes show physiological age transition (from blue to green, from green to red).
The structure also illustrates a reiteration (in blue).
Comments
-
1. In the GreenLab modelling approach, the physiological age is not related to the axis but to
the phytomer (and the growth unit).
As the axis develops, the terminal bud may change its physiological age. On a given axis, physiological age transitions are thus possible, but always in the same way of ageing, from the lower physiological age to the higher one.
2. To simplify, in the GreenLab approach, total reiteration is only allowed on physiological age 1. In other words, the physiological age of the branched axis is higher (classic branching) or equal (reiteration) to the phytomer bearer's physiological age.
3. Branching order. Note that the branching order (the rank given by the number of branchings from the current phytomer position to the seed) is not the physiological age. Defining structural simulations based on the branching order (such was the case of first AMAP simulations in the 80s) does not allow easy implementation and modelling of morphological gradients and reiterations.
Bibliography
Barthélémy, D., Caraglio, Y. 2007. Plant Architecture: A Dynamic, Multilevel and Comprehensive Approach to Plant Form, Structure and Ontogeny. Annals of Botany, 99 (3) : pp. 375-407 19 (access to paper and pdf)
Definition
Physiological Age (of a meristem)
Botany. Relates to the degree of differentiation of the structures produced by the meristem. It can be defined by a combination of morphological, anatomical and functional attributes of resulting entities. Notion introduced by Barthélémy and Caraglio (2007).Definition
