Preliminary Course
Botany. Architectural Analysis
Architectural Unit
The physiological age
-
While describing the various elementary botanical entities (phytomer, growth unit, annual shoot) ,
their differentiations should be examined according three gradients in time, called
chronological, ontogenetic and physiological ages, respectively.
- The chronologic age or calendar age corresponds simply to the period (i.e. year, month, week or day of formation for instance) in which the elementary botanical entity was edified.
- The ontogenetic age refers to the elapsed time after seed germination (the ontogenetical time unit considered may be a year, a day or a growth cycle according to the specific complexity and growth pattern of the species).
- The physiological age of a meristem refers to the degree of differentiation
of the structures it has produced.
The physiological age may be estimated a posteriori by a non-limitative series of qualitative and quantitative criteria.
For example, the short axes of many trees are typical features of physiologically aged structures: growth units are short, bear flowers and have a short lifetime.
These highly differentiated axes may be considered as physiologically old whatever their moment of appearance.
By contrast, main axes consisting of vigorous growth units and/or annual shoots may be considered as physiologically young products and generally appear only in the young tree.
On architectural units showing a clear axis typology, the physiological age is set as an index of this typology, starting from 1 to the trunk (if monopodial), up to the brachyblasts, given the highest physiological age.
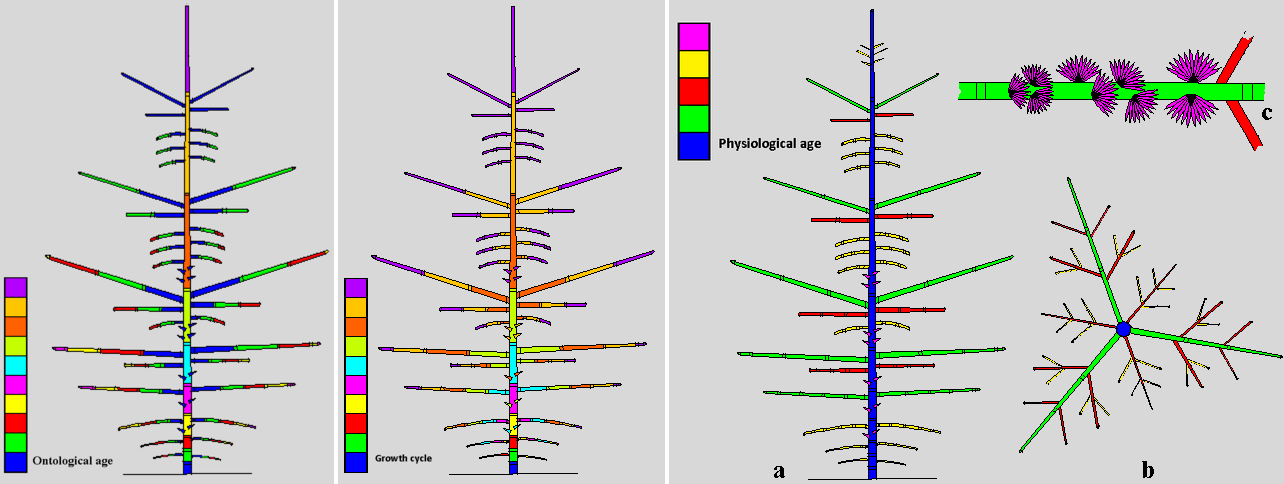
Age identifications on diagrammatic representations of Cedrus atlantica (Drawings S. Sabatier, CIRAD)
Left: chronological ages, defined from the successive growth sequences.
Middle: ontogenetic ages, defined from the successive growth sequences, relative to the axis appearance date.
Right: physiological ages, defined from the axis typology.
a) tree elevation view, b) view of a tier of branches, c) view of a branch annual shoot bearing a short shoot.
The identification for a botanical entity of these three ages is fundamental for understanding the comprehensive architecture of a plant or even its plasticity, i.e. the effects of the environment on its development and structure.
It permits the precise characterization of all elementary levels of organization within the more integrative individual architecture and allows a precise multi-level description of plant architecture and organization.
Bibliography
Barthélémy, D., Caraglio, Y. 2007. Plant Architecture: A Dynamic, Multilevel and Comprehensive Approach to Plant Form, Structure and Ontogeny. Annals of Botany, 99 (3) : pp. 375-407 19 (access to paper and pdf)
Definition
