GreenLab Course
Development
Simulating plant organogenesis
The different levels of botanical plant structural elements (i.e. growth units, axis, architectural unit, and reiteration) can be generated using a dual scale automaton (Zhao, X. et al, 2001).
Micro-states
-
The phytomer (metamer), the fundamental structural unit of the plant body, is attached
to a micro-state. In order to reflect the botanical typology, several micro-states
usually need to be defined for a given physiological age.
A common usual framework leads to a micro-state Mii,a being defined from both the physiological age of the internode (i) and the physiological age of its axillary bud (a).
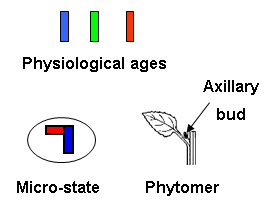
Physiological ages, metamer and micro-state (Drawing X. Zhao, LIAMA, CASIA)
- The physiological age of the micro-state internode's is 1,
while the physiological age of its axillary bud is 3.
At a given physiological age, a simple automaton can generate a growth unit (or a full axis portion in case of continuous growth) thanks to micro-state successions.
A growth unit is thus defined by a list of micro-states with their occurrences.
A micro-state sequence building a growth unit is called a macro-state
In the following example, this macro-state could be codified as:
((Mi1,3, 2) , (Mi1,2,1) ), describing a growth unit of three metamers of physiological age 1, respectively bearing axillary buds of physiological ages 3, 3, and 2.

Micro-states, and a growth unit (Drawing X. Zhao, LIAMA, CASIA)
- The automaton generates the sequence ((Mi1,3, 2) , (Mi1,2,1) )
and builds a macro-state, representing a growth unit.
Bibliography
Zhao, X., De Reffye, P., Xiong, F. L., Hu, B. G., & Zhan, Z. G. 2001. Dual-scale automaton model for virtual plant development. The Chinese Journal of Computers, 24(60), pp. 608-617
Definition
