Preliminary Course
Botany. Architectural Analysis
Architectural Unit
Morphogenetic gradients
-
At whole plant level, the morphogenetic gradients notion was defined by
(Barthélémy et al.,1997a) in order to take into account the intrinsic organization rules of plant
structure and was shown to be a powerful in explaining the observed structure and series of modifications of botanical
entities during the ontogeny of any plant species.
- In the establishment growth phase of any plant grown from seed, a base effect gradient can usually be observed, related to the gradual appearance of more vigorous axes.
- Acrotony: within annual shoots and growth units of most rhythmically growing trees, an increasing acropetal gradient of lateral axes vigour can often be observed.
- Drift: decreasing vigour can be observed as a general feature linked with axis ageing;
- sequential reiteration stands for the automatic duplication of the sequence of development and associated gradients of the main axis by another axis.
- the base effect is a gradient linked to the establishment growth phase;
- acrotony, with an increasing gradient of lateral axis vigour, is common in rhythmically growing trees;
- drift is a general feature related to axis ageing;
- reiteration, stands for the duplication of the sequence of development.
These morphogenetic gradients reflect the various processes of differentiation related to morphogenetic repetition phenomena that can be identified in plant construction:
These gradients can be summarized in the following figure:
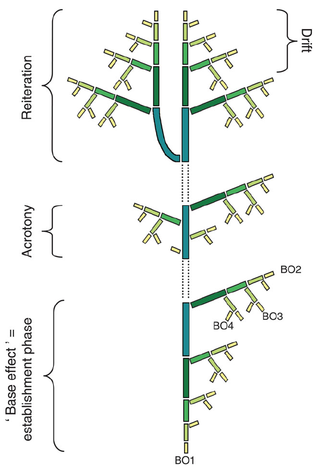
Morphogenetic gradients (after Barthélémy et al.,1997a).
-
Theoretical and diagrammatic representation of the distribution of elementary botanical entities with
similar characteristics (i.e. presenting the same physiological properties and represented by the same size and
colour rectangle on the diagram) according to some main morphogenetic gradients very commonly observed in
seed plants.
For the initial structure and reiterated complexes four branching orders are illustrated (BO1 to BO4), BO1 representing the main axis;
Bibliography
Edelin C. 1977. Images de l'architecture des conifères. Thèse de Doctorat (Sciences biologiques option Biologie végétale). Université de Montpellier II, 255 p.
Barthélémy, D., Edelin, C., Hallé, F. 1991. Canopy architecture, in: Raghavendra A.S. (Ed.), Physiology of trees, John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, 1991, pp. 1-20
Definition
Architectural Unit
Botany. The architectural Unit of a given plant species is the specific expression of its architectural model. The architectural Unit of a plant can be seen as a hierarchical branched system in which the axes can be grouped into categories according to their morphological, anatomical or functional distinctive features (Barthélémy et Caraglio, 2007).See also: Architectural Model.
