Preliminary Course
Botany. Architectural Analysis
Plant organization
Phytomers and the leafy axis levels
-
The fundamental structural unit of the plant body is called a
phytomer or metamer.
A phytomer is formed by a node with its leaf (or leaves), its axillary bud(s) and the subtending node.
Successive phytomers derived from a terminal bud thus build a leafy axis.
By way of its elementary growth process, a plant is made up of a succession of phytomers.
Each node carries one or more leaves.
Two successive nodes derived from a given meristem are separated by an internode.
An axillary bud can be found in the axil of each leaf.
The set of successive phytomers derived from a given meristem expresses a physical direction, an axis carrying leaves: the leafy axis.
The tip of the axis carries the apical meristem (apical bud, also called terminal bud), while axillary buds, in leaf axils, allow branching.
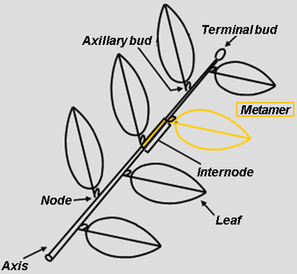
The leafy axis (drawing D. Barthélémy, CIRAD)
The leafy axis results from successive phytomers (or metamers) arising from apical bud growth and development.
In yellow: a metamer with its internode, its node, leaf and axillary bud.
Definition
