Preliminary Course.
Plant and crop Models
Example
THe authors share a long history in plant modelling, from the late seventies to nowadays, developing various plant structural and functional structural models
Computational models
-
Starting in the late seventies, the first developments by Ph. de Reffye on Coffea
led to the definition of a
structural or geometrical plant growth model called AMAP.
This model became popular for various applications including Computer Graphics.

Structural 3D plant simulations
- Left : Benson plotter 4-colour drawing(1984)
Right: Silicon Graphics simulated Cypress (1990).
(Images P. de Reffye and M. Jaeger, CIRAD)
In the late eighties, the structure was used as a transport pathway support to host functional aspects, such as leaf evapotranspiration and secondary growth, building a Functional Structural Plant Model (FSPM).

An FSPM implementation: tha Amap Para Software P. de Reffye, F. Blaise, 1993
- Plant structure, leaf evapotranspiration and secondary growth simulation.
(Illustrations P. de Reffye and F. Blaise, CIRAD)
These approaches were computational:
The structure is simulated applying rules of development defined from field observations.
Mathematical models
-
The next model generation, developed in cooperation with China, called GreenLab ,is a
mathematical model.
It differs from computational models in that development and functional processes are described by equations and do not strictly result from simulation.
The model therefore quantifies the structure (the number of organs, their appearance time, etc.) without requesting an exhaustive structural implementation.
This plant model is therefore seen as a classic mathematical dynamic model.
Such an approach makes the model reversible, making parameter identification and optimization more affordable.
In its latest developments, GreenLab can provide functional feedback on the structure under various environmental conditions.
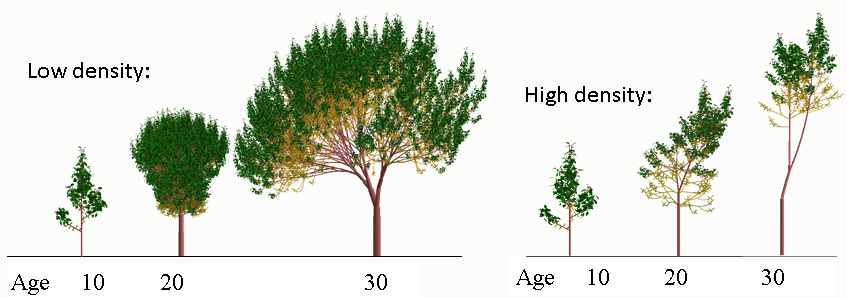
Plant structure plasticity due to density simulated by the GreenLab Model
- This example shows three tree growth stages under two different densities.
The underlying concept is the Projection Area, which thresholds branching and axis lengthening in structural development.
(Images © Digiplante software, A. Mathieu and P.H. Cournède, Ecole Centrale of Paris, 2007)
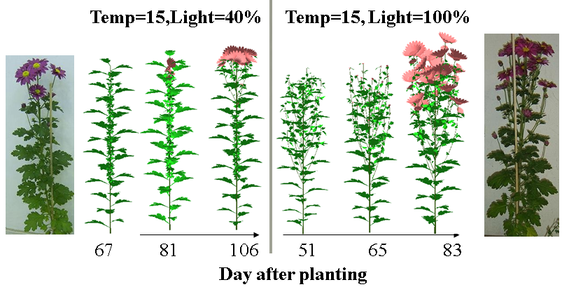
Plant structure plasticity due to environmental conditions simulated by the GreenLab Model
- This example shows three Crysanthemium growth stages under two different light and temperature conditions.
(Photos and illustrations with © GreenScilab software, M.G. Kang, LIAMA-CASIA)
Definition
SPM (Structural Plant Model)
Modelling. (abrev.) Stands for "Structural Plant Model", or "Geometrical Plant Model". Qualifies a mathematical or computational model that expresses the plant architecture (the structure) dynamics thru the development. Such a model offers usually a 3D output.Definition
FSPM (Functional Structural Plant Model)
Modelling. (abrev.) Stands for "Functional Structural Plant Model". Qualifies a mathematical or computational model that expresses both the plant architecture (the structure) dynamics thru the development and its production dynamics thru the organ geometrical development.Definition
