GreenLab Course
Production-Expansion
Photosynthesis (reminder)
Light Use Efficiency
In agronomy, the result of photosynthesis activity, i.e. biomass production, is simply quantified by weight.
-
It has been shown that the biomass growth rate, expressed in grams of dry matter per square metre per day
(g.m-2.d-1) is linearly related to absorbed irradiance (MJ.m-2.d-1)
for a wide range of crop communities.
This relationship between biomass growth and absorbed irradiance (PAR) defines Light Use Efficiency, abbreviated as LUE.
Note. When considering total irradiance, this ratio is called Radiation Light Use Efficiency, abbreviated as RUE.
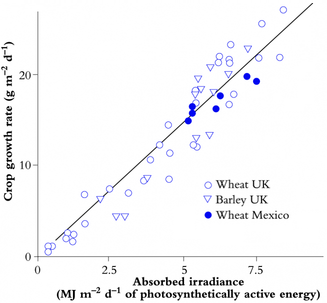
Light Use Efficiency on common crops.
-
Light Use Efficiency (in g.MJ-1) is represented by the slope of this relationship.
It is equivalent to 3 g.MJ-1 in this example (based on Evans 1993).
Hence, when LUE and the irradiance exposure are known, a simple growth crop model can be defined.
A simple LUE Model
On a daily basis, dry biomass growth can be expressed as follows:
-
dW = LUE . PAR . (1 - e-k LAI)
where:
-
dW = biomass growth rate ( in g.m-2.d-1)
LUE = light use efficiency ( in g.MJ-1)
k = extinction coefficient
LAI = leaf area index
PAR = Photosynthetic Active Radiation incident on the crop (MJ.m-2.d-1)
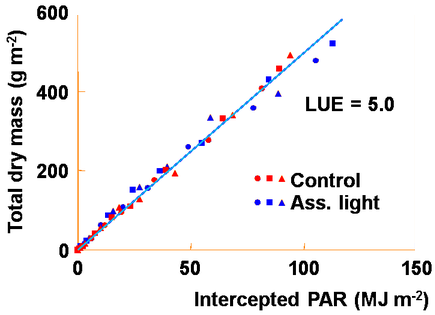
Light use efficiency reported in winter on 3 plant densities with and without light assimilation for cut chrysanthemum. (Graph E. Heuvelink, WAGENINGEN UNIVERSITY)
1. Many applications assume constant LUE values as show in the above figure, but LUE can be made dependent on CO2, temperature, light intensity, etc.
2. In the GreenLab model, LUE is defined from the fresh biomass weight, on the basis of 80% water concentration.
Definition
LUE (Light Use Efficiency)
Physiology (abrev.). LUE defines the conversion factor between the daily dry biomass production, expressed in gramme per squere meter per day and the absorbed irradiance (PAR) expressed in Mega Joule per square meter per day. Unit: g.MJ-1. See also: PAR, RUEDefinition
PAR (Photosynthetically Active Radiation)
Physiology (abrev.). PAR defines the wave band of solar radiation that plants are able to use in the process of photosynthesis. In agronomy, PAR is usually expressed in energy units as an irradiance per area. Unit: W.m-2.Definition
