GreenLab Course
Development
Architectural Botanical reminders.
Plant growth and development result from the meristem activity.
Structure establishment results from primary growth, while branch thickness results from secondary growth.
The Leafy Axis
The fundamental structural unit of the plant body is called a phytomer or metamer.
A metamer is formed by a node with its leaf (or leaves), its axillary bud(s) and
the subtending node.
Successive phytomers formed from a terminal bud build an axis.
Axillary buds, at the axils of leaves, allow branching.
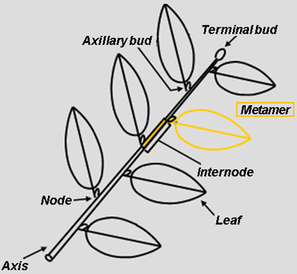
The leafy axis (Drawing D. Barthélémy, CIRAD)
- A leafy axis is built from successive phytomers formed from the apical (terminal) bud
A phytomer is defined by an internode and various organs branched on it, including leaves.
Axillary buds, enabling branching, are located in the leaf axils.
-
In many species (for instance temperate) the edification of an axis is due to a rhythmic growth process.
The axis is thus built from several growth units.
Considering the growth unit is an important key for modelling, since some architectural patterns are defined at this level, such as the branching pattern.
Important facts to consider for modelling aspects
-
The leafy axis is a construction built from successive discrete elements: phytomers.
Continuous growth must be distinguished from the rhythmic case. In rhythmic growth, axis construction must occur on two scales: first the construction of the growth unit from successive phytomers, then the succession of growth units.
Branching potential must be considered at phytomer level.
A phytomer enables several types of branching (since several organs may arise from it).
Bibliography
Barthélémy, D., Caraglio, Y. 2007. Plant Architecture: A Dynamic, Multilevel and Comprehensive Approach to Plant Form, Structure and Ontogeny. Annals of Botany, 99 (3) : pp. 375-407 19 (access to paper and pdf)
Definition
Metamer (Phytomer)
Botany. Botanical entity formed by a node, associated with its leaf (or leaves) and axillary bud(s) plus the subtending internode. First defined by White, 1979.Definition
Primary growth
Botany. Primary growth is the growth that occurs as a result of cell division at the tips of stems and roots, and that gives rise to primary tissue building axes.The primary growth of a plant is the result of several processes that can be grouped into two distinct, but coordinated morphogenetic events: organogenesis and extension (Champagnat et al., 1986).
Definition
